Objective: To investigate the effects of normalizing vitamin D levels (≥20 ng/ml) on renal function indicators in patients with type 2 diabetes. Methods: Sixty-six patients with type 2 diabetes were enrolled. After vitamin D supplementation, vitamin D levels, urinary microalbumin-to-creatinine ratio (UACR), and estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) were measured. Based on post-supplementation vitamin D levels, patients were divided into normal vitamin D level group (≥20 ng/ml) and vitamin D deficiency group (<20 ng/ml). Differences in UACR and eGFR between the two groups were compared. Results: The eGFR in the normal vitamin D level group was significantly higher than that in the vitamin D deficiency group, while the UACR in the normal vitamin D level group was significantly lower than that in the vitamin D deficiency group (P < 0.05). Conclusions: Normalization of vitamin D levels (≥20 ng/mL) in patients with type 2 diabetes may be associated with improved renal function indicators.
| Published in | Science Discovery (Volume 13, Issue 6) |
| DOI | 10.11648/j.sd.20251306.20 |
| Page(s) | 166-169 |
| Creative Commons |
This is an Open Access article, distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, provided the original work is properly cited. |
| Copyright |
Copyright © The Author(s), 2025. Published by Science Publishing Group |
Vitamin D, Type 2 Diabetes, Glomerular Filtration Rate, Urinary Microalbumin-to-creatinine Ratio
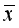 ±SD表示,否则以四分位数Q50(Q25, Q75)表示;两组数据如符合正态性,则采用参数检验t检验,否则选用非参数检验Mann-Whitney 检验;分类资料采用卡方(χ2)检验。P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
±SD表示,否则以四分位数Q50(Q25, Q75)表示;两组数据如符合正态性,则采用参数检验t检验,否则选用非参数检验Mann-Whitney 检验;分类资料采用卡方(χ2)检验。P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。 组别 | 维生素D水平正常组 | 维生素D水平缺乏组 | 统计值 |
血清25-羟基维生素D(ng/mL) | 28.61[24.16,33.43] | 16.39[12.72,18.14] | t= -6.7 P<0.001 |
年龄(岁) | 57.60±11.63 | 58.00±12.80 | t=0.3,P=0.90 |
性别(男/女,例) | 24/18 | 8/16 | χ2=3.47,P=0.06 |
组别 | 维生素D水平正常组 | 维生素D水平缺乏组 | 统计值 |
肾小球滤过率(ml·min-11.73m-2) | 82.19±14.37 | 68.96±25.61 | t= -2.3,P=0.03 |
尿微量白蛋白/肌酐比值(mg/g) | 2.13[0.76,4.77] | 5.10[1.45,24.00] | t= -2.35,P=0.02 |
| [1] | 中华医学会糖尿病学分会. 中国2型糖尿病防治指南(2020年版)[J]. 中华内分泌代谢杂志, 2021. 37(04): 311-398. |
| [2] | 肖丹. 2型糖尿病患者25羟维生素D3水平与糖尿病肾病相关性分析[M]. 2020, 南方医科大学. |
| [3] | Xiao X, Wang Y, Hou Y, et al. Vitamin D deficiency and related risk factors in patients with diabetic nephropathy[J]. J Int Med Res, 2016. 44(3): 673-84. |
| [4] | Liyanage P, Lekamwasam S, Weerarathna T.P, et al. Effect of Vitamin D therapy on urinary albumin excretion, renal functions, and plasma renin among patients with diabetic nephropathy: A randomized, double-blind clinical trial[J]. J Postgrad Med, 2018. 64(1): 10-15. |
| [5] | 李丹丹, 金佳培, 王元元. 25羟基维生素D3与2型糖尿病患者肾功能指标的相关性分析[J]. 实用医技杂志, 2025. 32(5): 377-380. |
| [6] | 马世凤, 彭定琼, 段俊婷. 25羟维生素D对住院2型糖尿病患者肾功能的影响[J]. 中国保健营养, 2019. 29(35): 64. |
| [7] | 吴珊珊, 张丹凤, 戚仁娟, 等. 血清25-羟维生素D水平及糖化血红蛋白与糖尿病肾脏疾病的相关性研究[J]. 临床肾脏病杂志, 2025. 25(9): 727-734. |
| [8] | 中国营养学会健康管理分会. 维生素D营养状况评价及改善专家共识[J]. 中华健康管理学杂志 %J Chinese Journal of Health Management. 2023. 17(4): 245-252. |
| [9] | Feng M, Lv J, Huang F.T, et al. Vitamin D deficiency in patients with stages 1 and 2 chronic kidney disease in Southern China[J]. Niger J Clin Pract, 2018. 21(12): 1639-1644. |
| [10] | Feng M, Lv J, Huang F.T, et al, Predictors of Vitamin D deficiency in predialysis patients with stage 3-5 chronic kidney diseases in Southern China[J]. Niger J Clin Pract, 2017. 20(10): 1309-1315. |
| [11] | Lei M, Liu Z, and Guo J. The Emerging Role of Vitamin D and Vitamin D Receptor in Diabetic Nephropathy[J]. Biomed Res Int, 2020: 4137268. |
| [12] | Souza C.S, Deluque A.L, Oliveira B.M, et al. Vitamin D deficiency contributes to the diabetic kidney disease progression via increase ZEB1/ZEB2 expressions[J]. Nutr Diabetes, 2023. 13(1): 9. |
| [13] | Esfandiari A, Pourghassem Gargari B, Noshad H, et al. The effects of vitamin D(3) supplementation on some metabolic and inflammatory markers in diabetic nephropathy patients with marginal status of vitamin D: A randomized double blind placebo controlled clinical trial[J]. Diabetes Metab Syndr, 2019. 13(1): 278-283. |
| [14] | 程昌琴, 杨若梅, 李志勇, 等. 2型糖尿病患者血清25-羟维生素D3与肾功能的关系分析 [J]. 重庆医学, 2016. 45(25): 3491-3492, 3495. |
| [15] | 田俊红, 邹远征, 杨翠玲. 维生素D辅助胰岛素治疗妊娠期糖尿病的临床疗效[J]. 西北药学杂志, 2023. 38(5): 114-118. |
| [16] | Huang Y, Yu H, Lu J, et al. Oral supplementation with cholecalciferol 800 IU ameliorates albuminuria in Chinese type 2 diabetic patients with nephropathy[J]. PLoS One, 2012. 7(11): e50510. |
APA Style
Qiuju, L., Qin, Y., Hui, L. (2025). Effects of Normalizing Vitamin D Levels on Glomerular Filtration Rate and Urinary Microalbumin-to-Creatinine Ratio in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Science Discovery, 13(6), 166-169. https://doi.org/10.11648/j.sd.20251306.20
ACS Style
Qiuju, L.; Qin, Y.; Hui, L. Effects of Normalizing Vitamin D Levels on Glomerular Filtration Rate and Urinary Microalbumin-to-Creatinine Ratio in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Sci. Discov. 2025, 13(6), 166-169. doi: 10.11648/j.sd.20251306.20
@article{10.11648/j.sd.20251306.20,
author = {Lyu Qiuju and Yang Qin and Li Hui},
title = {Effects of Normalizing Vitamin D Levels on Glomerular Filtration Rate and Urinary Microalbumin-to-Creatinine Ratio in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
},
journal = {Science Discovery},
volume = {13},
number = {6},
pages = {166-169},
doi = {10.11648/j.sd.20251306.20},
url = {https://doi.org/10.11648/j.sd.20251306.20},
eprint = {https://article.sciencepublishinggroup.com/pdf/10.11648.j.sd.20251306.20},
abstract = {Objective: To investigate the effects of normalizing vitamin D levels (≥20 ng/ml) on renal function indicators in patients with type 2 diabetes. Methods: Sixty-six patients with type 2 diabetes were enrolled. After vitamin D supplementation, vitamin D levels, urinary microalbumin-to-creatinine ratio (UACR), and estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) were measured. Based on post-supplementation vitamin D levels, patients were divided into normal vitamin D level group (≥20 ng/ml) and vitamin D deficiency group (<20 ng/ml). Differences in UACR and eGFR between the two groups were compared. Results: The eGFR in the normal vitamin D level group was significantly higher than that in the vitamin D deficiency group, while the UACR in the normal vitamin D level group was significantly lower than that in the vitamin D deficiency group (P < 0.05). Conclusions: Normalization of vitamin D levels (≥20 ng/mL) in patients with type 2 diabetes may be associated with improved renal function indicators.},
year = {2025}
}
TY - JOUR T1 - Effects of Normalizing Vitamin D Levels on Glomerular Filtration Rate and Urinary Microalbumin-to-Creatinine Ratio in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes AU - Lyu Qiuju AU - Yang Qin AU - Li Hui Y1 - 2025/12/29 PY - 2025 N1 - https://doi.org/10.11648/j.sd.20251306.20 DO - 10.11648/j.sd.20251306.20 T2 - Science Discovery JF - Science Discovery JO - Science Discovery SP - 166 EP - 169 PB - Science Publishing Group SN - 2331-0650 UR - https://doi.org/10.11648/j.sd.20251306.20 AB - Objective: To investigate the effects of normalizing vitamin D levels (≥20 ng/ml) on renal function indicators in patients with type 2 diabetes. Methods: Sixty-six patients with type 2 diabetes were enrolled. After vitamin D supplementation, vitamin D levels, urinary microalbumin-to-creatinine ratio (UACR), and estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) were measured. Based on post-supplementation vitamin D levels, patients were divided into normal vitamin D level group (≥20 ng/ml) and vitamin D deficiency group (<20 ng/ml). Differences in UACR and eGFR between the two groups were compared. Results: The eGFR in the normal vitamin D level group was significantly higher than that in the vitamin D deficiency group, while the UACR in the normal vitamin D level group was significantly lower than that in the vitamin D deficiency group (P < 0.05). Conclusions: Normalization of vitamin D levels (≥20 ng/mL) in patients with type 2 diabetes may be associated with improved renal function indicators. VL - 13 IS - 6 ER -